Collaboration Between Tech and Road Transport Authorities (in cities and national level): AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance for Traffic Infrastructure
December 18, 2025

Traffic infrastructure is the backbone of modern road transport authorities, yet traditional maintenance approaches often lead to costly emergency repairs, unexpected road closures, and compromised safety.
The shift from reactive to predictive maintenance—powered by artificial intelligence and sensor networks—represents a major opportunity for municipalities to modernize infrastructure management.
By leveraging real-time data from sensors deployed across road networks, city authorities can anticipate failures before they occur, schedule proactive interventions, and significantly reduce both costs and disruptions to traffic flow.
The Challenge of Traditional Infrastructure Maintenance
Conventional traffic infrastructure maintenance typically relies on reactive responses or fixed maintenance schedules. While familiar, these approaches present several critical challenges:
Unexpected Failures and Safety Risks
Infrastructure failures often occur without warning, creating hazardous conditions for road users. Traffic signal malfunctions, rapidly forming potholes, or structural degradation can lead to accidents and injuries, forcing authorities into urgent response mode.
High Emergency Repair Costs
Emergency repairs can cost two to three times more than planned maintenance. Crews must be mobilized at short notice—often outside regular working hours—while materials are procured urgently. Indirect costs further compound the burden, including traffic congestion, detour management, and increased citizen complaints.
Traffic Disruptions and Inefficient Resource Use
Unplanned road closures are a major contributor to congestion, accounting for an estimated 15–20% of non-recurring traffic delays in large metropolitan areas. At the same time, calendar-based maintenance may service assets that are still in good condition, while overlooking components nearing critical failure.
How AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Works
Predictive maintenance transforms infrastructure management through a set of integrated technological components:
Sensor Deployment and Data Collection
Modern traffic infrastructure can be equipped with sensors that continuously monitor asset conditions. These include pavement sensors with embedded strain gauges, bridge health monitoring systems measuring vibration and corrosion, traffic signal diagnostics, environmental sensors, and computer vision cameras capable of detecting surface defects and damage.
Real-Time Data Processing and Predictive Analytics
Machine learning algorithms analyze incoming sensor data in real time, establishing baseline conditions and detecting anomalies. AI models trained on historical failure patterns and current observations can predict when specific infrastructure components are likely to fail. These predictions account for wear trends, environmental stress, traffic intensity, and interdependence between components — providing not only alerts but also estimated timelines with confidence intervals.
Automated Alert Generation
When the system identifies an elevated risk of failure, it automatically generates prioritized alerts. These are ranked according to safety criticality, time to failure, potential impact, repair complexity, and available budget—allowing authorities to act decisively and efficiently.
Case Study: The EvoRoads Project in Latvia
A compelling example of successful collaboration between technology providers and public authorities is the EvoRoads pilot project in Latvia, which demonstrates the real-world impact of AI-driven predictive maintenance.
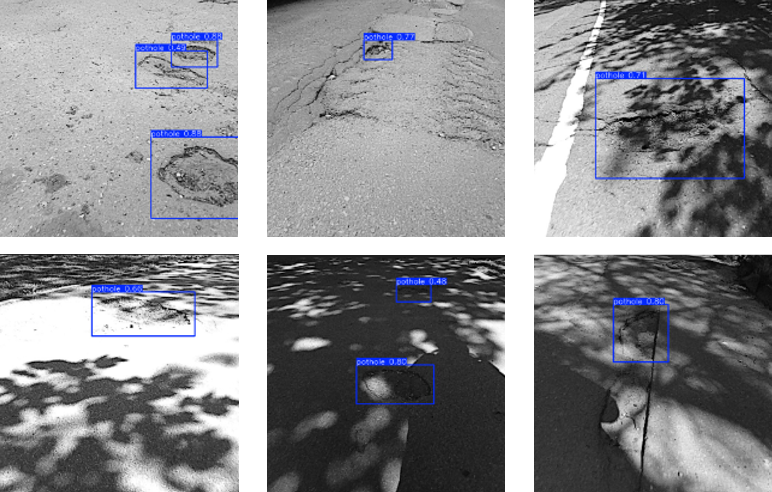
About the EvoRoads Project
EvoRoads (Evolutionary Solutions for Realising a Holistic Safe System Approach for All Road Users) is an EU Horizon Europe initiative launched in May 2024 and running until April 2027. Bringing together 20 partners across Europe, with pilot sites in Spain, Italy, Latvia, and Romania, the project supports the EU’s Vision Zero objective of eliminating road fatalities by 2050.
Latvia’s Pilot: Automated Infrastructure Monitoring
The Latvian demonstration site, implemented in collaboration with Riga City Council and local partners, focuses on automated, low-cost infrastructure monitoring for road hotspots, bridges, and tunnels. Key objectives include early identification of road sections prone to rapid deterioration and proving that advanced monitoring solutions do not have to be prohibitively expensive.
Fits Traffic’s Role and Practical Applications
As a technology partner in the EvoRoads consortium, Fits Traffic delivers AI-powered traffic analytics and computer vision capabilities that integrate seamlessly with Riga City Council’s existing traffic management systems.
The pilot also incorporates digital twin technology for critical infrastructure assets, proactive warning systems for maintenance teams, and a comprehensive framework of 124 safety indicators covering infrastructure condition, traffic management, and the protection of vulnerable road users. Regular co-creation workshops with Riga City Council ensure the solutions align with real operational needs.



Future Implications
EvoRoads enables authorities to predict equipment overloads and defects before they occur, making it possible to upgrade capacity proactively or introduce traffic management measures to reduce structural stress. The low-cost approach validated in Riga provides a scalable and replicable model for municipalities across Europe and beyond.
Case Study: WIM Project in Latvia
Client
The Latvian State Roads performs the management of the state road network, administration of the State Road Fund and organization of public procurement in order to provide the public with profitable, durable, safe and environmentally friendly state road network.
The challenge
It’s a common understanding that overweight vehicles pose risks to road infrastructure and safety. Total weight, axle loads and spacing of the vehicle is crucial for road structures such as bridges and others, while the axle and axle group loads are crucial for pavements. Almost a third of the full traffic flow on the main Latvian roads come from the Heavy Goods Vehicles and the problem with overweight vehicles on the national roads became evident. Periodically organized manual traffic controls confirmed that the laws were not abided by many carriers, but the scope of the issue was hard to estimate precisely due to a lack of automated and efficient approach towards monitoring the full traffic flow for overweight vehicles.
The solution
Fits Traffic implements a back-office solution that would integrate WIM sensors and ANPR cameras to automatically capture photographic evidence of all the overweight vehicles (recording gross vehicle weight and axle loads). The solution also provided information on the full traffic, which enabled the client to evaluate the overweight vehicle data in the context of the complete traffic flow. Fits.safety system is used to facilitate the pre-selection process and to gather necessary evidence data. It is then prepared for delivery to the responsible road-safety authority for further violation processing purposes.
Additional Examples from Around the World
Predictive maintenance is already delivering measurable results globally:
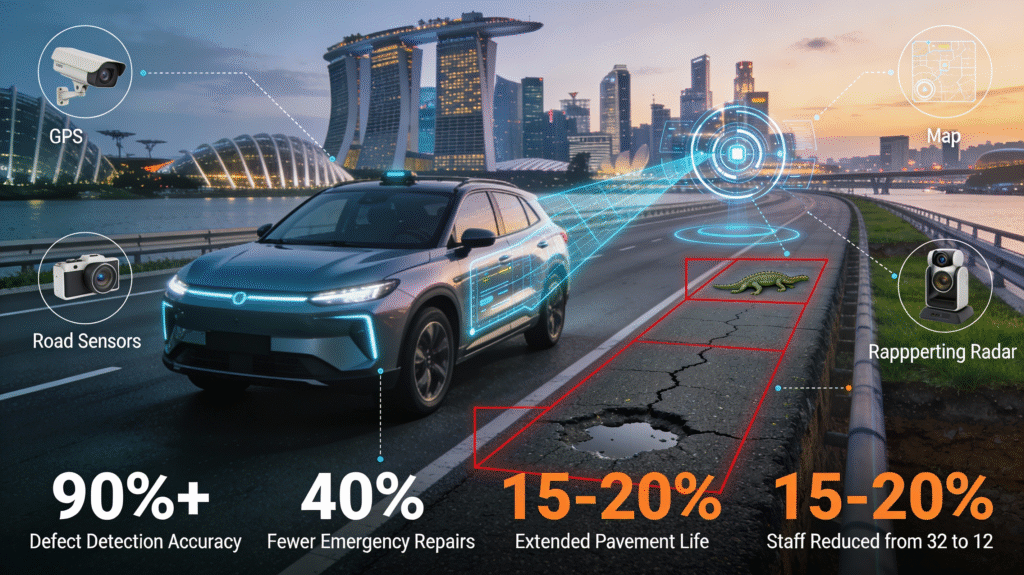
- Singapore: The Land Transport Authority uses AI-driven analysis of road sensor data and ground-penetrating radar, reducing emergency repairs by 40% and extending pavement life by 15–20%. LTA’s Road Maintenance Management System (RMMS) integrates AI, video analytics, GPS, and mapping to scan roads from inspection vehicles, achieving over 90% accuracy in defect detection such as potholes, alligator cracks, and damaged pavements. This replaced manual inspections that required 32 personnel, now reduced to 12, with real-time alerts dispatching teams via apps for faster repairs.
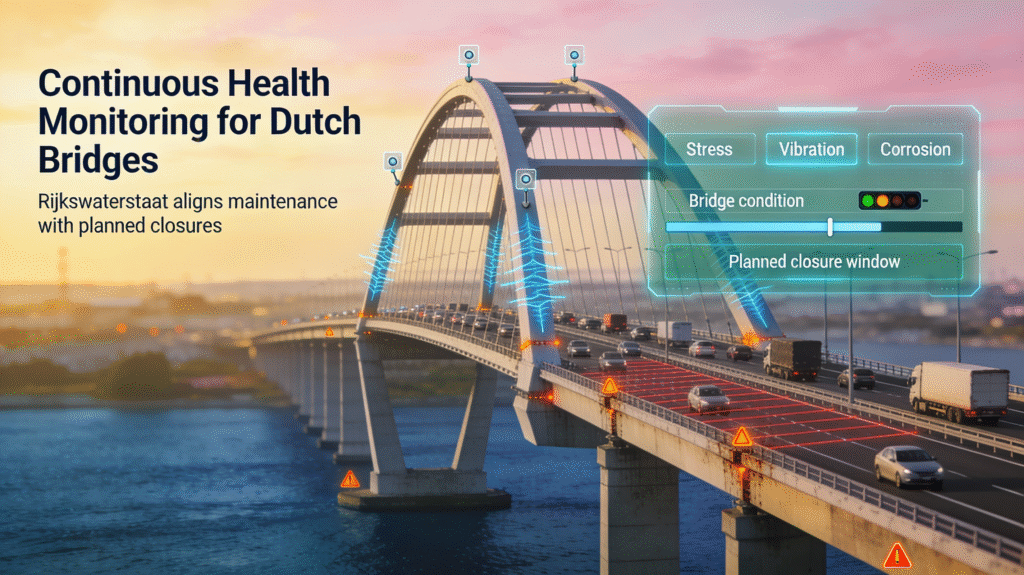
- The Netherlands: Continuous bridge health monitoring on major structures tracks stress, vibration, and corrosion, enabling maintenance to be aligned with planned closures. Rijkswaterstaat, the national infrastructure agency, faces a large “replacement and renovation” wave for hundreds of aging bridges, so it is investing in continuous monitoring to keep structures safe while avoiding unplanned closures. Many Dutch bridges are reaching or exceeding their original design life, making real‑time condition data critical to decide when to strengthen, renovate or replace them.
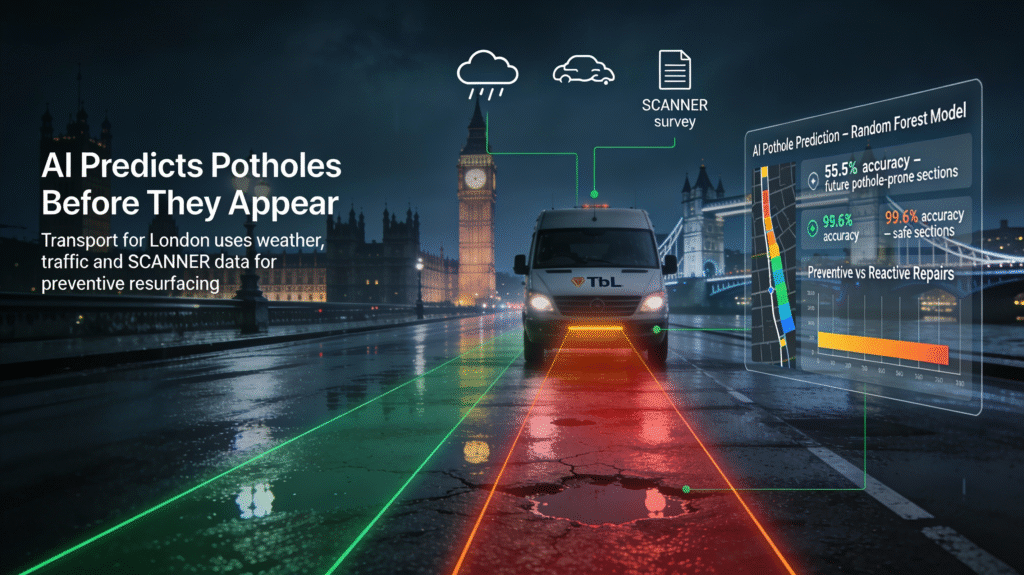
- London: Transport for London pilots AI systems that predict pothole formation using weather and traffic data, enabling preventive surface treatments. The initiative draws from SCANNER surveys—standard UK road condition assessments—combined with TfL’s pothole records from 2017-2020, using machine learning like Random Forest to predict defects based on nine key indicators such as cracking, rutting, and texture depth. These models achieved 55.5% accuracy in spotting future pothole-prone sections and 99.6% for safe ones, aiding budget allocation for preventive resurfacing over reactive fixes.
The Role of Technology Companies and Road Transport Authorities
Successful predictive maintenance programs depend on close collaboration, with each party contributing essential expertise.
Technology Company Responsibilities
Technology providers deliver sensor deployment, AI platform development, system integration, continuous algorithm improvement, and technical support to help interpret and act on insights.
City Authority Responsibilities
Municipalities contribute historical maintenance data to train AI models, define local maintenance priorities, execute recommended interventions, document outcomes, and allocate resources to both digital platforms and field operations.
A Collaborative Framework
The most effective initiatives are built on ongoing dialogue—regular performance reviews, pilot testing of new technologies, and steering committees that bring together traffic engineers, maintenance supervisors, IT specialists, and technology partners.
Benefits for Road Transport Authorities
Transitioning to predictive maintenance delivers substantial and measurable benefits. Total infrastructure costs can be reduced by 20–35% compared to reactive approaches, while preventing a single major bridge failure can save millions in emergency repairs. Early issue detection improves safety for both road users and maintenance workers. Planned interventions during off-peak hours reduce traffic delays caused by roadworks by up to 40–50%. At the same time, data-driven planning improves workforce efficiency, supports long-term mobility strategies, and reduces environmental impact through fewer delays and longer asset lifecycles.
Implementation Challenges
Despite its advantages, predictive maintenance presents several challenges. Initial investment in sensor networks and AI platforms must be balanced against long-term savings. Integrating real-time data with legacy systems often requires significant IT effort. Organizations must also manage cultural change through training and adoption programs. Cybersecurity is critical to protect connected infrastructure, and early deployments may produce false positives until algorithms are fully calibrated to local conditions.
Conclusion
AI-driven predictive maintenance marks a fundamental shift in how cities manage traffic infrastructure. By moving from reactive responses to proactive, data-informed decision-making, municipalities can enhance safety, reduce costs, minimize disruptions, and extend the lifespan of critical assets.
The EvoRoads project in Latvia exemplifies how European research initiatives, technology companies such as Fits Traffic, and municipal authorities like Riga City Council can work together to deliver practical innovation in urban mobility. As infrastructure continues to age worldwide, cities that adopt predictive maintenance early will gain a competitive edge in fiscal sustainability, citizen satisfaction, and transportation system performance.
At Fits Traffic, we provide end-to-end solutions that integrate sensor networks, AI analytics, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Our collaborative approach ensures technology serves the real operational needs of transportation authorities—enabling smarter, safer, and more cost-effective infrastructure stewardship.
References
- EvoRoads Project – Horizon Europe Initiative (Grant Agreement No. 101147850): https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/101147850; https://evoroads-project.eu/,
- ERTICO ITS Europe – EvoRoads Project Launch and Objectives: https://www.ertico.com/what-we-do/european-projects/evoroads,
- Riga City Council – Spatial Planning and Mobility Department;
- Singapore Land Transport Authority – Smart Maintenance Systems: https://www.openinnovationnetwork.gov.sg/innovation-challenges/developing-singapore-road-pavement-performance-system-(pps); https://www.mot.gov.sg/news-resources/newsroom/opening-speech-by-senior-minister-of-state-for-transport–dr-amy-khor–at-the-6th-its-singapore-summit-2024/,
- Netherlands Ministry of Infrastructure – Bridge Health Monitoring Program: Design Validation via Infrastructure Health Monitoring of the Circular Bridge Project,
- Transport for London – AI-Driven Road Condition Assessment: https://takes.jamesomalley.co.uk/p/ai-pothole-tech-is-good; Transport for London supports innovation to tackle road congestion | Computer Weekly,
- European Commission – Smart Maintenance for Transport Infrastructure: Smart mobility – Mobility and Transport – European Commission.